16S rRNA Sequencing vs Shotgun Metagenomics: Which Method is Right for Your Research?
Dr. Sharma faced a critical decision. Her research grant had just been approved to study the gut microbiome's role in childhood obesity across 200 samples. She had funding, samples ready for collection, and an ambitious timeline—but she couldn't decide between two fundamentally different approaches: 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing or shotgun metagenomic sequencing. The choice would determine not just her budget allocation but the very questions she could answer about microbial communities.
Like Dr. Sharma, thousands of researchers across India face this pivotal decision when planning microbiome studies. Both 16S rRNA sequencing and shotgun metagenomics reveal the hidden world of microbial communities, but they differ dramatically in approach, cost, depth of information, and analytical complexity. Choose correctly, and you maximize research insights within budget constraints. Choose incorrectly, and you either overspend for unnecessary data or miss critical biological information your study requires.
This comprehensive guide cuts through the confusion, comparing 16S rRNA sequencing and shotgun metagenomics across every dimension that matters for your research—from fundamental principles and cost structures to taxonomic resolution, functional capabilities, and practical considerations that determine which method suits your specific scientific questions.
Understanding the Fundamental Difference
Before diving into comparisons, understanding what each method actually does clarifies why they serve different research purposes.
What is 16S rRNA Sequencing?
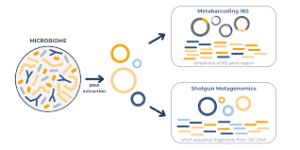
16S rRNA sequencing takes a targeted approach, amplifying and sequencing only the 16S ribosomal RNA gene—a specific genetic marker present in all bacteria and archaea. This gene contains nine hypervariable regions (V1-V9) that differ between bacterial species, functioning as a "barcode" for bacterial identification.
Think of 16S sequencing as conducting a census. You're counting who's present in the community and their relative abundances, but you're not examining what they're doing or what capabilities they possess beyond their identity.
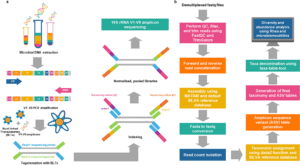
The Process:
-
Extract DNA from your sample (gut, soil, water, etc.)
-
Use universal bacterial primers to amplify the 16S rRNA gene
-
Sequence millions of these amplified gene copies
-
Compare sequences to reference databases
-
Identify bacterial taxa present and their relative abundances
What You Learn:
-
Which bacteria and archaea are present
-
Their relative proportions in the community
-
Community diversity metrics
-
Taxonomic composition down to genus (sometimes species) level
What You Don't Learn:
-
Functional capabilities of the community
-
Metabolic pathways present
-
Antibiotic resistance genes
-
Viruses, fungi (though ITS sequencing targets fungi separately)
-
Strain-level differences within species
What is Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing?
Shotgun metagenomics takes an unbiased approach, randomly fragmenting and sequencing ALL DNA present in your sample—bacterial genomes, archaeal genomes, viral DNA, fungal DNA, even host contamination.
Think of shotgun metagenomics not just as conducting a census but also as surveying everyone's skills, jobs, tools, and social networks. You learn not just who's there but what they're capable of doing.
The Process:
-
Extract DNA from your sample
-
Fragment all DNA into short pieces (no amplification step)
-
Sequence millions of these random DNA fragments
-
Assemble fragments into longer sequences
-
Identify genes, match to reference genomes, assign taxonomy
-
Annotate functions, pathways, resistance genes, virulence factors
What You Learn:
-
Taxonomic composition (bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, eukaryotes)
-
Functional gene content and metabolic potential
-
Complete or partial microbial genomes
-
Antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factors
-
Strain-level resolution within species
-
Horizontal gene transfer events
-
Mobile genetic elements (plasmids, transposons)
What You Don't Learn (Directly):
-
Which genes are actively expressed (requires RNA-Seq)
-
Viability of microorganisms (DNA from dead cells persists)
Cost Comparison: Budget Reality Check
Cost often represents the decisive factor when choosing between these methods, particularly for large-scale studies or budget-constrained academic research.
16S rRNA Sequencing Costs in India
Standard Pricing: ₹3,500 - ₹6,000 per sample
This competitive pricing makes 16S sequencing accessible for large sample sets common in microbiome research. At Yaazh Xenomics, 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing costs approximately ₹4,000-₹5,000 per sample including library preparation, sequencing, and basic bioinformatics analysis.
What's Included:
-
DNA quality assessment
-
PCR amplification of 16S gene (typically V3-V4 or V4 region)
-
Library preparation with barcoding for multiplexing
-
Illumina MiSeq or NextSeq sequencing (50,000-100,000 reads per sample)
-
Demultiplexing and quality filtering
-
Basic taxonomic classification
-
Alpha and beta diversity analysis
-
Taxonomy tables and abundance charts
Cost Breakdown for a Typical Study:
-
50 samples: ₹2,00,000 - ₹3,00,000
-
100 samples: ₹4,00,000 - ₹6,00,000
-
200 samples: ₹8,00,000 - ₹12,00,000
Volume Discounts: Most laboratories including Yaazh Xenomics offer 10-20% discounts for projects with 50+ samples, making large-scale studies more affordable.
Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Costs in India
Standard Pricing: ₹15,000 - ₹30,000 per sample
Shotgun metagenomics costs significantly more due to much higher sequencing depth requirements, complex library preparation, and computationally intensive analysis.
Pricing Tiers:
Shallow/Taxonomic Profiling: ₹15,000-₹18,000 per sample
-
5-10 million reads per sample
-
Adequate for taxonomic profiling
-
Limited functional analysis
Standard Functional Analysis: ₹22,000-₹28,000 per sample
-
20-40 million reads per sample
-
Comprehensive taxonomic profiling
-
Functional gene analysis
-
Pathway reconstruction
Deep Sequencing/Genome Assembly: ₹35,000-₹50,000 per sample
-
50-100+ million reads per sample
-
De novo genome assembly
-
Strain-level analysis
-
Complete functional characterization
Cost Breakdown for a Typical Study:
-
50 samples (standard depth): ₹11,00,000 - ₹14,00,000
-
100 samples (standard depth): ₹22,00,000 - ₹28,00,000
-
200 samples (standard depth): ₹44,00,000 - ₹56,00,000
Cost-Per-Information Analysis
While shotgun metagenomics costs 4-6 times more per sample than 16S sequencing, it provides exponentially more information. The question becomes: do you need that additional information for your research questions?
Cost Efficiency Scenarios:
16S is More Cost-Effective When:
-
Large sample sizes (100+ samples)
-
Primary question is "who's there?"
-
Comparing community composition across conditions
-
Budget constraints limit total project spend
-
Quick pilot studies before deeper investigation
Shotgun is More Cost-Effective When:
-
Functional questions are critical
-
Small, focused sample sets
-
Strain-level resolution required
-
Antibiotic resistance profiling needed
-
Multiple data types from single investment (taxonomy + function + resistance + virulence)
Example: If your ₹10 lakh budget allows either 200 samples with 16S or 40 samples with shotgun metagenomics, choose based on whether biological variation (requiring many samples) or functional depth (requiring comprehensive data per sample) matters more for your research question.
Taxonomic Resolution: How Deep Can You See?
The taxonomic resolution—how precisely you can identify microorganisms—differs substantially between these methods.
16S rRNA Sequencing Taxonomic Resolution
Kingdom/Domain: 100% accurate (bacteria vs archaea)
Phylum: Excellent resolution (>95% accuracy)
Class/Order/Family: Very good resolution (85-95% accuracy)
Genus: Good resolution (70-85% accuracy)
-
Most 16S studies reliably identify to genus level
-
Variable regions differ in genus-level discrimination ability
Species: Limited and variable (30-70% accuracy)
-
Some species are distinguishable
-
Many species within the same genus share nearly identical 16S sequences
-
Cannot reliably differentiate closely related species
-
Example: E. coli and Shigella species are indistinguishable by 16S
Strain: Not possible with 16S sequencing
-
Cannot distinguish different strains of the same species
-
Example: Cannot differentiate probiotic Lactobacillus strains from pathogenic strains
Limitations:
-
Horizontal gene transfer has moved 16S genes between unrelated bacteria, causing misclassification
-
Reference database completeness affects identification accuracy
-
Multiple 16S copies per genome (varies by species) creates quantification challenges
-
PCR amplification biases favor certain bacterial groups
Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Taxonomic Resolution
All Levels: Excellent resolution when sufficient depth is achieved
Kingdom/Domain: 100% accurate across bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, and eukaryotes
Phylum through Family: Excellent resolution (>95% accuracy)
Genus and Species: Excellent resolution (>90% accuracy)
-
Uses multiple genes and whole genome information
-
Distinguishes closely related species reliably
-
Example: Clearly separates E. coli from Shigella species
Strain: Possible with adequate sequencing depth
-
Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) distinguish strains
-
Can identify specific pathogenic strains
-
Example: Differentiates E. coli O157:H7 from commensal E. coli strains
-
Requires deeper sequencing (50M+ reads) for robust strain calling
Unclassified/Novel Organisms:
-
Better handles novel or poorly characterized organisms
-
Assembly-based approaches can reconstruct genomes from unknown species
-
Metagenomic assembled genomes (MAGs) expand our understanding of uncultured bacteria
Viruses and Fungi:
-
Shotgun metagenomics detects bacteriophages, viruses, and fungi
-
16S misses these completely (except with separate ITS sequencing for fungi)
-
Critical for comprehensive microbiome understanding
Quantification Accuracy:
-
More accurate quantification (no PCR amplification bias)
-
Single copy core genes provide better abundance estimates
-
Cell lysis efficiency still affects results but less than PCR bias
Practical Implications of Resolution Differences
When Genus-Level is Sufficient (Choose 16S):
-
Exploring overall community structure
-
Comparing phylum/class level shifts
-
Identifying major taxonomic changes
-
Large-scale population studies
-
Environmental surveys
When Species/Strain-Level is Critical (Choose Shotgun):
-
Pathogen identification and source tracking
-
Probiotic strain verification
-
Antibiotic resistance profiling (strain-specific)
-
Outbreak investigations
-
Precision microbiome interventions
Example Study: Investigating gut microbiome changes in diabetic patients compared to healthy controls. If your hypothesis involves phylum-level dysbiosis (Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes ratio shifts), 16S suffices. If you're tracking specific Akkermansia muciniphila strains that correlate with metformin response, shotgun metagenomics is essential.
Functional Analysis: What Are They Doing?
Perhaps the most critical distinction between these methods lies in functional information—understanding what microbial communities are capable of doing, not just who's present.
16S rRNA Sequencing Functional Capabilities
Direct Functional Information: None
16S rRNA genes encode ribosomal RNA, not functional proteins. Sequencing 16S tells you nothing directly about metabolic capabilities, antibiotic resistance, or virulence.
Indirect Functional Prediction:
Tools like PICRUSt2 (Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States) attempt to infer functional potential based on taxonomic composition. The logic: if you know which bacteria are present, you can predict their likely gene content based on reference genomes of related organisms.
Limitations of Functional Prediction:
-
Accuracy decreases for poorly characterized organisms
-
Cannot detect horizontal gene transfer events
-
Misses strain-level functional variation
-
Predictions are statistical averages, not actual measurements
-
Cannot identify novel genes or pathways
-
Prediction accuracy: 60-80% for well-characterized communities, lower for novel environments
When Functional Prediction Works Reasonably:
-
Well-studied environments (human gut)
-
Dominant taxa with sequenced reference genomes
-
Broad pathway-level questions
-
Generating hypotheses for follow-up studies
When Functional Prediction Fails:
-
Novel or poorly characterized environments
-
Organisms without closely related reference genomes
-
Strain-specific functions (antibiotic resistance often strain-specific)
-
Precise quantification of specific genes
-
Pathogenicity factors requiring exact gene identification
Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Functional Capabilities
Direct Functional Information: Comprehensive
Shotgun metagenomics sequences all genes present in your sample, providing direct measurement of functional potential.
Metabolic Pathways:
-
Identify complete metabolic pathways present in communities
-
Carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid synthesis, vitamin production
-
Nitrogen fixation, sulfur cycling, methane production
-
Secondary metabolite biosynthesis
-
Quantify relative abundance of pathway genes
Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs):
-
Detect known resistance genes across all antibiotic classes
-
Quantify resistance gene abundance
-
Identify mobile genetic elements carrying resistance
-
Track resistance gene spread in populations
-
Critical for clinical, agricultural, and environmental studies
Virulence Factors:
-
Identify toxins, adhesins, secretion systems
-
Assess pathogenic potential of communities
-
Important for food safety and clinical diagnostics
Stress Response Genes:
-
Metal resistance genes
-
Detoxification enzymes
-
Heat/cold shock proteins
-
Osmotic stress response
Biosynthetic Gene Clusters:
-
Natural product discovery
-
Industrial enzyme identification
-
Biotechnology applications
CRISPR Systems:
-
Bacterial defense mechanisms
-
Historical phage exposure records
-
Microbiome engineering targets
Horizontal Gene Transfer:
-
Plasmids, transposons, integrons
-
Track gene mobility in communities
-
Understand resistance gene dissemination
Novel Gene Discovery:
-
Identify previously unknown genes
-
Expand functional annotations
-
Biotechnology innovation
Functional Analysis Comparison Table
| Functional Aspect | 16S rRNA Sequencing | Shotgun Metagenomics |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Pathways | Predicted (60-80% accuracy) | Directly measured |
| Antibiotic Resistance | Not detected | Comprehensive detection |
| Virulence Factors | Not detected | Comprehensive detection |
| Novel Genes | Cannot discover | Discovery possible |
| Quantification | Inferred from taxonomy | Direct gene counts |
| Strain-Specific Functions | Not possible | Detected |
| Mobile Genetic Elements | Not detected | Detected and characterized |
| Pathway Completeness | Cannot assess | Can verify complete pathways |
Research Questions Requiring Functional Data
You Need Shotgun Metagenomics If:
-
Studying antibiotic resistance development or transmission
-
Investigating probiotic mechanisms of action
-
Identifying biotechnology enzymes in environmental samples
-
Understanding metabolic interactions between community members
-
Tracking virulence factors in clinical or food safety contexts
-
Discovering novel biosynthetic pathways
-
Assessing functional redundancy in communities
-
Validating functional predictions from 16S studies
Example: Studying the gut microbiome's role in dietary fiber fermentation and short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production. 16S identifies bacteria correlating with high SCFA levels, but only shotgun metagenomics reveals which specific genes and pathways generate SCFAs, enabling targeted probiotic or prebiotic interventions.
Bioinformatics and Data Analysis Complexity
The computational analysis required differs dramatically between these methods, affecting timelines, expertise requirements, and infrastructure needs.
16S rRNA Sequencing Bioinformatics
Analysis Complexity: Moderate
Standard Analysis Pipeline:
-
Quality Control: FastQC assessment, adapter trimming
-
Denoising/Clustering: DADA2 (ASVs) or UPARSE (OTUs)
-
Taxonomic Assignment: Naive Bayes classifier against reference databases (SILVA, Greengenes, RDP)
-
Diversity Analysis: Alpha diversity (Shannon, Simpson, Chao1), Beta diversity (Bray-Curtis, UniFrac)
-
Statistical Testing: PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, differential abundance (DESeq2, LEfSe)
-
Visualization: PCoA plots, taxonomic barplots, heatmaps
Popular Analysis Platforms:
-
QIIME2: Most popular, user-friendly GUI available
-
Mothur: Comprehensive, command-line based
-
DADA2 (R package): Modern approach using exact sequence variants
Computational Requirements:
-
RAM: 8-16 GB sufficient for most studies
-
Storage: 10-50 GB per project
-
Processing Time: Hours to 1-2 days for typical study
-
Skills Required: Basic command-line proficiency or GUI navigation
-
Learning Curve: 1-2 weeks to run standard pipelines
Data Size:
-
Raw data: 50-200 MB per sample
-
Processed results: Small (CSV tables, metadata)
Bioinformatics Support:
Many service providers including Yaazh Xenomics include standard 16S bioinformatics analysis (taxonomy tables, diversity metrics, basic statistics) in sequencing costs, delivering publication-ready results.
Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Bioinformatics
Analysis Complexity: High to Very High
Standard Analysis Pipeline:
-
Quality Control: FastQC, adapter trimming, host genome removal
-
Taxonomic Profiling: MetaPhlAn, Kraken2, mOTUs2
-
Functional Profiling: HUMAnN, MEGAN, DIAMOND
-
Assembly: MEGAHIT, metaSPAdes (for MAG recovery)
-
Gene Calling: Prodigal, MetaGeneMark
-
Annotation: Prokka, eggNOG-mapper, KEGG, COG databases
-
Binning (MAG Recovery): MetaBAT, MaxBin, CONCOCT
-
Specialized Analysis: Antibiotic resistance (CARD, ResFinder), Virulence (VFDB), Plasmids, Phages
-
Statistical Analysis: Same as 16S for taxonomy, plus functional pathway statistics
Computational Requirements:
-
RAM: 64-256 GB minimum, often requiring high-memory servers
-
Storage: 50-500 GB per sample (raw data), terabytes for large studies
-
Processing Time: Days to weeks for comprehensive analysis
-
Skills Required: Advanced bioinformatics, programming (Python/R), Unix/Linux expertise
-
Learning Curve: Months to proficiency, requires dedicated bioinformatician
Data Size:
-
Raw data: 10-50 GB per sample (standard depth)
-
Assembled contigs: 5-20 GB per sample
-
Annotation databases: 100+ GB
Infrastructure Needs:
-
High-performance computing cluster
-
Large storage systems
-
Backup and archival solutions
Cost of Analysis:
In-house bioinformatics requires dedicated personnel (₹50,000-₹1,00,000+ per month for skilled bioinformatician) plus computing infrastructure. Many researchers outsource complex metagenomic analysis to service providers, adding ₹8,000-₹15,000 per sample to sequencing costs.
Bioinformatics Support:
Comprehensive service providers like Yaazh Xenomics offer complete metagenomic bioinformatics including taxonomic profiling, functional annotation, pathway analysis, resistance gene screening, and custom analyses tailored to research questions.
Time from Sample to Results
16S rRNA Sequencing:
-
Sequencing: 5-7 days
-
Standard analysis: 3-5 days
-
Total: 10-14 days from sample to publication-ready results
Shotgun Metagenomics:
-
Sequencing: 7-10 days
-
Standard analysis: 7-14 days
-
Advanced analysis (assembly, MAGs): 2-4 weeks additional
-
Total: 2-6 weeks from sample to comprehensive results
Sample Requirements and Technical Considerations
Practical laboratory aspects influence method selection, particularly sample type, DNA quantity requirements, and technical challenges.
DNA Quality and Quantity Requirements
16S rRNA Sequencing:
-
Minimum DNA: 10-50 ng total
-
Quality: Moderate quality acceptable (partially degraded DNA works)
-
Purity: A260/A280 ratio >1.6 acceptable
-
PCR amplification compensates for low input and quality issues
Shotgun Metagenomics:
-
Minimum DNA: 500 ng-1 µg (10-20x more than 16S)
-
Quality: High-quality DNA required (intact, high molecular weight)
-
Purity: A260/A280 ratio 1.8-2.0 preferred
-
No amplification step means library quality directly affects results
Practical Implication: Samples with limited DNA (clinical swabs, environmental samples with low biomass) often work for 16S but fail shotgun metagenomics quality control. Low biomass samples may show high host DNA contamination in shotgun approaches.
Sample Types and Challenges
Both Methods Work Well:
-
Fecal/stool samples (abundant microbial DNA)
-
Gut biopsy tissue
-
Oral swabs
-
Soil with high microbial load
-
Wastewater
16S Preferred for Challenging Samples:
-
Low biomass samples (blood, cerebrospinal fluid, typically sterile sites)
-
Degraded DNA (archaeological samples, forensic samples)
-
Samples with high host DNA contamination
-
Limited sample volume
Shotgun Metagenomics Challenges:
-
Host DNA Contamination: Human/animal samples contain 90-99% host DNA. Shotgun sequences everything, wasting reads on host genome. Host DNA depletion adds complexity and cost.
-
Sequencing Depth: Low abundance organisms require very deep sequencing for detection. 16S amplification democratizes detection across abundance ranges.
-
Complex Communities: Extremely diverse communities (soil, marine) require immense sequencing depth for comprehensive coverage.
Technical Biases
16S rRNA Sequencing Biases:
-
PCR Amplification Bias: Primers favor certain bacterial groups, underrepresenting others
-
Copy Number Variation: Different bacteria have 1-15 copies of 16S gene, affecting quantification
-
Extraction Bias: Cell wall differences affect lysis efficiency (Gram-positive harder to lyse)
-
Primer Mismatch: Universal primers don't amplify all bacteria equally
Shotgun Metagenomics Biases:
-
Extraction Bias: Still present (affects both methods)
-
Library Preparation Bias: GC content affects library amplification
-
Sequencing Bias: Some DNA sequences amplify preferentially
-
Less systematic bias overall compared to PCR-based methods
Choosing the Right Method: Decision Framework
With fundamental differences understood, systematic decision-making ensures you select the optimal method for your specific research.
Choose 16S rRNA Sequencing When:
Your Primary Research Questions Are:
-
Who is present in my microbial community?
-
How does community composition differ between groups?
-
Which taxa correlate with phenotypes or conditions?
-
What is the overall diversity of my samples?
-
How do communities cluster based on taxonomy?
Your Study Characteristics Include:
-
Large sample size: 50+ samples (budget constraints favor 16S)
-
Exploratory studies: Initial microbiome characterization
-
Pilot studies: Generating preliminary data for grant applications
-
Low biomass samples: Limited DNA availability
-
Degraded samples: Archaeological, forensic, or poorly preserved samples
-
Time-sensitive projects: Need results quickly (2 weeks)
Your Resources Are:
-
Limited budget: ₹5-10 lakh total for 100-200 samples
-
Basic bioinformatics: Utilizing provider's standard analysis
-
Standard computing: Desktop/laptop sufficient for secondary analysis
Example Research Projects:
-
Population-scale microbiome surveys (IBD, obesity, diabetes cohorts)
-
Environmental monitoring across many sites
-
Time-series studies with frequent sampling
-
Screening for microbiome-phenotype associations
-
Agricultural soil microbiome monitoring
Choose Shotgun Metagenomics When:
Your Primary Research Questions Are:
-
What functional capabilities does my microbial community possess?
-
Which metabolic pathways are present/active?
-
What antibiotic resistance genes exist in my samples?
-
Can I identify pathogenic strains?
-
What virulence factors are present?
-
How do functional profiles differ between groups?
-
Can I recover complete or partial genomes from my samples?
Your Study Characteristics Include:
-
Moderate sample size: 20-50 samples (manageable cost for comprehensive data)
-
Hypothesis-driven: Specific functional questions to address
-
Clinical/diagnostic: Pathogen identification, resistance profiling
-
Biotechnology: Novel enzyme or gene discovery
-
Mechanistic studies: Understanding how microbiomes affect hosts
-
Strain-level resolution: Distinguishing closely related organisms
Your Resources Are:
-
Adequate budget: ₹10-50 lakh for 30-100 samples at standard depth
-
Bioinformatics expertise: Access to skilled bioinformatician or outsourcing capability
-
Computing infrastructure: High-performance computing available
Example Research Projects:
-
Probiotic mechanism of action studies
-
Antibiotic resistance surveillance
-
Food safety pathogen detection
-
Novel antimicrobial discovery from environmental samples
-
Microbiome-metabolite association studies
-
Functional validation of 16S-identified associations
-
Precision microbiome interventions
Hybrid Approach: Best of Both Worlds
Many sophisticated studies use BOTH methods strategically:
Sequential Strategy:
-
Phase 1: 16S sequencing of all samples (100-200) - identify taxonomic patterns, select interesting samples
-
Phase 2: Shotgun metagenomics on subset (20-30) - functional validation, mechanistic insights
Benefits:
-
Cost-effective screening with 16S
-
Functional depth where it matters most
-
Comprehensive understanding (taxonomy + function)
-
Stronger publications combining approaches
Example: Studying gut microbiome in treatment-responsive vs non-responsive cancer immunotherapy patients. 16S sequences all 150 patients, identifies taxonomic signatures. Shotgun metagenomics on 15 responders and 15 non-responders reveals functional pathways (bile acid metabolism, vitamin synthesis) explaining treatment response.
Combined Budget: ₹6 lakh (150 samples × ₹4,000) + ₹7 lakh (30 samples × ₹23,000) = ₹13 lakh total. More affordable than shotgun-only approach (₹34.5 lakh for 150 samples).
Real Research Scenarios: Which Method Would You Choose?
Scenario 1: Gut Microbiome in Type 2 Diabetes
Study Design: 200 diabetic patients vs 200 healthy controls, analyzing fecal samples
Research Question: Does gut microbiome composition differ between diabetic and healthy individuals?
Recommendation: 16S rRNA Sequencing
Rationale:
-
Large sample size (400 total) - cost prohibitive with shotgun (₹80-100 lakh vs ₹16-20 lakh)
-
Primary question is taxonomic (who's different?)
-
Sufficient power for statistical detection of compositional differences
-
Can predict broad functional differences (SCFA production) if needed
-
Budget allows comprehensive sampling across demographics
Follow-up: If specific taxa correlate strongly with diabetes, shotgun metagenomics on subset validates functional mechanisms.
Scenario 2: Antibiotic Resistance in Hospital Wastewater
Study Design: Monitoring resistance genes in hospital wastewater over 6 months (monthly samples from 5 hospitals = 30 samples)
Research Question: What antibiotic resistance genes are present and how do they change over time?
Recommendation: Shotgun Metagenomics
Rationale:
-
Primary question is functional (resistance genes)
-
16S cannot detect resistance genes
-
Need to identify mobile genetic elements carrying resistance
-
Moderate sample size (30) makes shotgun affordable (₹6.5-8 lakh)
-
Public health implications require precise resistance gene identification
-
Can track resistance gene transmission between bacterial hosts
Why Not 16S: Would identify bacteria present but miss critical resistance gene information needed for public health surveillance.
Scenario 3: Soil Microbiome Response to Organic Farming
Study Design: Comparing soil microbiomes from 50 organic farms vs 50 conventional farms
Research Question: How does farming practice affect soil microbial diversity and community structure?
Recommendation: 16S rRNA Sequencing
Rationale:
-
Large sample size (100 samples)
-
Primary question is compositional change
-
Soil communities extremely diverse - shotgun requires prohibitive depth
-
Budget-friendly approach (₹4-5 lakh vs ₹22-28 lakh)
-
Can predict functional differences related to nitrogen cycling, carbon metabolism
-
Established 16S reference databases for soil bacteria
Optional Enhancement: Shotgun metagenomics on 10-15 most divergent samples (extreme organic vs extreme conventional) to validate functional predictions and discover novel enzymes.
Scenario 4: Probiotic Strain Verification and Quality Control
Study Design: Testing 20 commercial probiotic products to verify labeled strains and detect contaminants
Research Question: Do products contain advertised strains at claimed concentrations? Are contaminants present?
Recommendation: Shotgun Metagenomics
Rationale:
-
Requires strain-level identification (16S insufficient)
-
Need to detect bacterial, fungal, and viral contaminants
-
Quality control demands precise quantification
-
Small sample size (20 products) - affordable with shotgun (₹4-5.5 lakh)
-
Can verify functional genes associated with probiotic claims
-
Critical for regulatory compliance and consumer safety
Why Not 16S: Cannot distinguish probiotic strains from closely related species. Example: Cannot differentiate Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG from other L. rhamnosus strains.
Scenario 5: Oral Microbiome in Periodontal Disease
Study Design: 80 patients with periodontitis vs 80 healthy controls, comparing subgingival plaque
Research Question: How does oral microbiome differ in periodontal disease, and what pathways contribute to disease?
Recommendation: Hybrid Approach
Phase 1: 16S sequencing all 160 samples (₹6-8 lakh)
-
Identify taxonomic signatures of disease
-
Discover key discriminatory taxa
-
Assess diversity changes
Phase 2: Shotgun metagenomics on 40 samples (20 severe disease, 20 healthy controls) (₹10-12 lakh)
-
Functional pathways associated with disease
-
Virulence factors in pathogenic species
-
Biofilm formation genes
-
Host-microbe interaction mechanisms
Rationale:
-
Balanced approach maximizes both breadth (taxonomy) and depth (function)
-
Total budget ₹16-20 lakh provides comprehensive insights
-
Strengthens publication with complementary data types
-
Taxonomic and functional findings validate each other
Data Interpretation and Publication Impact
The scientific community and journals value different aspects of these methods depending on research context.
Publishing 16S rRNA Sequencing Studies
Strengths:
-
Well-established methodology with standardized protocols
-
Large sample sizes increase statistical power
-
Good for exploratory, descriptive, and correlational studies
-
Suitable for ecological and diversity-focused questions
Journal Expectations:
-
Adequate sequencing depth (30,000-50,000 reads per sample minimum)
-
Appropriate statistical methods for compositional data
-
Clear acknowledgment of limitations (genus-level resolution, functional predictions)
-
Proper negative controls addressing contamination
Common Criticisms:
-
"Functional predictions are not validated"
-
"Genus-level resolution insufficient for mechanistic claims"
-
"Correlation doesn't prove causation without functional data"
Ideal Applications:
-
Microbiome Journals: Microbiome, mSystems
-
Clinical Journals: Disease association studies
-
Ecological Journals: Environmental surveys, biogeography
-
Agricultural Journals: Soil, plant microbiome studies
Publishing Shotgun Metagenomic Studies
Strengths:
-
Provides mechanistic insights beyond correlation
-
Functional data supports causal hypotheses
-
Higher perceived scientific rigor
-
Novel gene/pathway discovery
-
Strain-level analysis adds precision
Journal Expectations:
-
Sufficient sequencing depth for claims (30M+ reads for functional, 50M+ for assembly)
-
Rigorous bioinformatics methods
-
Appropriate assembly and annotation tools
-
Validation of key findings (qPCR, metabolomics)
Common Criticisms:
-
"Small sample size limits generalizability"
-
"Sequencing depth insufficient for rare taxa"
-
"Functional potential doesn't equal functional activity" (need transcriptomics)
Ideal Applications:
-
High-Impact Journals: Nature, Science, Cell (mechanistic microbiome studies)
-
Specialized Journals: Nature Microbiology, Cell Host & Microbe
-
Clinical Journals: Pathogen genomics, resistance surveillance
-
Biotechnology Journals: Enzyme/gene discovery
Impact Factor Considerations
16S Studies:
-
Large cohorts (500+ samples) → High-impact clinical journals
-
Novel environments → Ecology journals
-
Methodological advances → Microbiome methods journals
Shotgun Studies:
-
Mechanistic insights → Highest impact journals
-
Clinical actionability → Major medical journals
-
Biotechnology discoveries → Applied journals
Hybrid Studies:
-
Often strongest publications
-
Complementary data types address reviewer concerns
-
Breadth (16S) + Depth (shotgun) = compelling narrative
Practical Workflow Recommendations
Translating method selection into actionable research planning ensures smooth project execution.
Starting a New Microbiome Project
Step 1: Define Core Research Questions
-
List primary questions driving study
-
Categorize as taxonomic, functional, or both
-
Prioritize by importance
Step 2: Assess Resource Constraints
-
Calculate total budget available
-
Determine sample size needs for statistical power
-
Evaluate bioinformatics access (in-house vs outsourced)
-
Consider timeline requirements
Step 3: Calculate Method Feasibility
-
16S Option: (Sample size × ₹4,500) + analysis time
-
Shotgun Option: (Sample size × ₹24,000) + extended analysis
-
Hybrid Option: (Large set × ₹4,500) + (Subset × ₹24,000)
Step 4: Pilot Study
-
Sequence 5-10 samples using chosen method
-
Verify DNA quality adequate
-
Confirm data quality meets expectations
-
Refine analysis approaches
-
Generate preliminary data for grants
Step 5: Consult Sequencing Provider
-
Discuss project specifics with experts
-
Optimize sampling strategy
-
Clarify deliverables and timelines
-
Understand bioinformatics support included
Working with Yaazh Xenomics
Yaazh Xenomics offers comprehensive microbiome sequencing services with expert guidance for method selection:
16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing:
-
₹4,000-₹5,000 per sample
-
V3-V4 or V4 region amplification
-
Illumina MiSeq/NextSeq sequencing
-
50,000-100,000 reads per sample
-
Complete bioinformatics analysis included
-
Taxonomy tables, diversity metrics, statistical testing
-
Publication-ready figures and reports
Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing:
-
₹22,000-₹28,000 per sample (standard depth)
-
Illumina NovaSeq/NextSeq sequencing
-
30-50 million reads per sample
-
Taxonomic profiling (species/strain level)
-
Functional annotation (KEGG, COG, CAZy)
-
Antibiotic resistance gene screening
-
Custom analysis for specific research questions
Additional Services:
-
Free pre-project consultation for method selection
-
Sample collection guidance and quality assessment
-
Customized analysis pipelines
-
Extended bioinformatics support
-
Data interpretation assistance
-
Pan-India sample collection services
Locations: Chennai, Coimbatore, Madurai, Mumbai, Pondicherry
Emerging Alternatives and Future Directions
The microbiome research field continues evolving with new technologies complementing or enhancing 16S and shotgun approaches.
Long-Read Sequencing
PacBio and Oxford Nanopore platforms generate reads spanning 10,000+ base pairs, enabling full-length 16S genes or complete bacterial genomes from metagenomic samples.
Advantages:
-
Full-length 16S improves species-level resolution
-
Better genome assembly from metagenomic data
-
Resolves repetitive genomic regions
Limitations:
-
Higher error rates (improving rapidly)
-
More expensive per base
-
Lower throughput
-
Emerging for microbiome applications
Metatranscriptomics
Sequencing RNA instead of DNA reveals which genes are actively expressed, addressing the "potential vs activity" limitation of shotgun metagenomics.
When to Add Metatranscriptomics:
-
Validating that predicted functions are actually active
-
Understanding dynamic responses to interventions
-
Time-course studies of microbial activity
-
Complementing shotgun metagenomics for complete picture
Metaproteomics and Metabolomics
Measuring proteins and metabolites directly assesses functional outputs of microbiomes.
Integration Strategy:
-
16S/Shotgun → who's there, what they can do
-
Metatranscriptomics → what they're expressing
-
Metaproteomics → what proteins they're making
-
Metabolomics → what metabolites they're producing
Multi-Omics Approach: Most comprehensive but expensive. Reserve for high-priority mechanistic studies.
Conclusion: Making Your Decision
Choosing between 16S rRNA sequencing and shotgun metagenomics represents one of the most consequential decisions in microbiome research project planning. The right choice aligns your research questions, budget constraints, sample characteristics, and analytical capabilities to maximize scientific impact.
Remember the Core Principles:
Choose 16S when your questions focus on taxonomic composition, you have large sample sizes requiring cost efficiency, you need rapid results, or you're conducting exploratory surveys building foundational knowledge.
Choose shotgun metagenomics when functional questions drive your research, strain-level resolution matters, you're identifying antibiotic resistance or virulence factors, or you need definitive mechanistic insights beyond correlation.
Consider hybrid approaches when budget allows—combining breadth and depth through strategic sequencing maximizes insights while managing costs.
For Dr. Sharma's childhood obesity study with 200 samples, the answer became clear: start with 16S sequencing across all participants to identify taxonomic signatures. Then, deploy shotgun metagenomics on 30 carefully selected samples representing extreme responder vs non-responder phenotypes to uncover functional mechanisms explaining why certain microbiomes correlate with obesity. This strategic approach provided comprehensive insights—taxonomic associations supported by mechanistic understanding—within her budget.
Your research deserves the same strategic thinking. Whether you're investigating clinical microbiomes, environmental communities, agricultural soil, or food microbiology, matching your method to your questions ensures you generate meaningful data advancing scientific knowledge.
Ready to start your microbiome research project? Contact Yaazh Xenomics today for expert consultation on 16S rRNA sequencing, shotgun metagenomics, or hybrid approaches tailored to your specific research needs. Our scientists help you design optimal sequencing strategies maximizing impact within your budget.
Call for free consultation or request detailed project quotes for your microbiome study.
Leave a Reply